It’s very common for medications to have unpleasant side effects that aren’t part of treating an ailment. Most of the time, these side effects are worth it due to the benefits of the medication.
One such medication that can cause a variety of side effects is gabapentin. The question is, can gabapentin cause hair loss, and if so, what can you do about it? Keep reading to learn more.
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is a medication approved by the Food and Drug Administration FDA to treat epilepsy in patients. It is also used as a treatment for neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome. It is a type of anticonvulsant that is often known under its variety of brand names, including Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. [1]
Gabapentin comes in various strengths, from 300mg to 800mg – the strength offered depends on the patient and their symptoms. The medication is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain, in turn stopping seizures. [2]
Does Gabapentin Cause Hair Loss?
Unfortunately, yes – in some cases, gabapentin can cause hair loss. Several articles have indicated that it is a known side effect, including one from the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management [3] that states a woman noticed significant hair loss in patchy areas of alopecia after taking 1800mg of gabapentin a day. Although, it should be noted that hair loss as a side effect is considered uncommon.
Hair loss caused by gabapentin is known as drug induced alopecia.
Why Does Gabapentin Sometimes Cause Hair Loss?
Right now, there is no clear reason why this anti seizure medication can cause hair loss. What is known is that gabapentin likely disrupts the hair growth cycle.
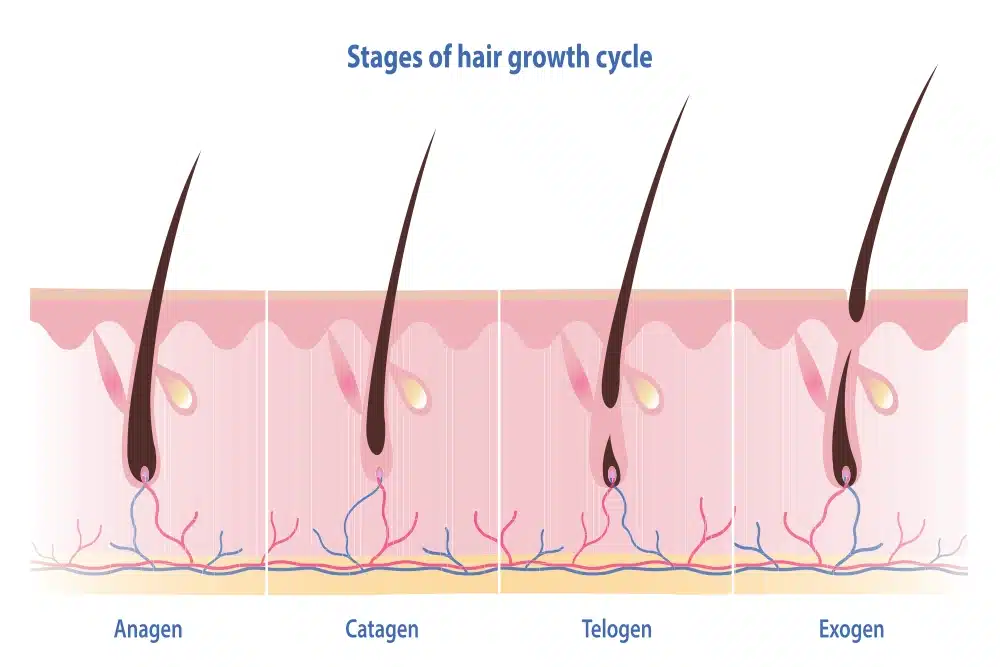
The hair growth cycle includes four distinct phases: the anagen phase (growth), the catagen phase (transition), the telogen phase (resting), and the exogen phase (shedding) [4]. Hair loss occurs when the hair growth cycle is disrupted, and the hair remains in the telogen and exogen phases for too long, leading to excessive shedding.
Drugs can cause a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, a type of hair loss caused by stress. Some drugs may also actively damage the hair follicles. The good news is that, in most cases, drug induced hair loss is temporary and completely reversible.
The Signs of Gabapentin Hair Loss
Are you worried that you have experienced the rare side effect of antiepileptic drugs – hair loss? Here are some of the signs.
Hair Shedding
The most obvious sign of hair loss caused by gabapentin is excessive shedding. Your hair sheds every day – this is a completely normal process. However, if you lose more than 150 hairs per day (which is often noticeable), that is a sign of drug induced hair loss. Often, this type of hair shedding leads to clogged drains and more hair being found on your pillow.
Patchy Spots on the Scalp
If you have patchy bald spots on the scalp, that is a clear sign of alopecia. These may be small and not very noticeable at first.
Thinner Hair
It’s not always clear that your hair is shedding. However, if you experience generally thinning hair, that could be an indication of gabapentin hair loss.
Hair Loss After Taking Gabapentin
It’s essential to recognize that hair loss is a common condition often caused by genetic factors. However, if the hair loss is experienced a few weeks or months after taking gabapentin, that’s a sign that the drug is causing the hair to fall out.
Is Gabapentin Hair Loss Permanent or Temporary?
Most of the time, hair loss due to antiepileptic medications like gabapentin is temporary, meaning it is reversible. Often, the hair grows back out again once a patient stops taking the medication.
Other Side Effects of Gabapentin
Hair loss is not the only side effect associated with gabapentin – in fact, there are many other more common side effects to be aware of, including:
- Sleepiness
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
- Dry Mouth
- Changes to Mood
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Weight Gain
- Joint Pain
- Swelling
Some side effects are more serious than others. In some cases, suicidal thoughts, allergic reactions, and pancreatitis can occur. If these symptoms occur, it’s crucial to consult a medical professional.
What to Do About Gabapentin Hair Loss
If you notice hair loss after taking gabapentin, your first instinct may be to stop taking the medication immediately. Here are some things you should do first, though.
Rule Out Other Causes of Hair Loss
It’s best to rule out other causes of hair loss first. Drug induced hair loss is not as common as other forms of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness). However, if the hair loss occurred not long after taking gabapentin, there’s a chance the drug did cause it.
Speak to Your Doctor
If you notice hair loss after taking gabapentin (as well as other unpleasant side effects), speak to your doctor. They can assess your medication situation and come up with an action plan to reduce symptoms.
Adjust the Dose
Your doctor may be able to adjust the dosage of your gabapentin prescription. By lowering the dose, you may still be able to take the drug without experiencing hair loss.
Switch Medications
Nobody wants to deal with hair loss. So, if gabapentin is causing your hair to fall out, consider asking your doctor to switch medications. There are other medications like gabapentin that can treat seizures (and other ailments).
Monitor Hair Growth
After switching your medication or dosage, begin monitoring your hair regrowth. This will give you a clear idea of what’s influencing and causing your hair loss. It helps to use a hair track app to do this.
Hair Loss Treatments
If your hair loss continues, rest assured there are several hair loss treatments that can help you regrow your locks once more.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a topical medication (although it is also available in oral form) that stimulates new hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp, allowing the hair follicles to receive the necessary nutrients for healthy hair growth. It is a medication you can get over the counter and is usually known by its brand name Rogaine. Both men and women can use it, and produces good results, as long as you use it daily. Stopping minoxidil can lead to the return of hair loss.
Finasteride
Another hair loss medication is finasteride. It is an oral medication that is typically used to treat enlarged prostates. It is only available to men via a prescription, and it cannot be obtained through the NHS for hair restoration purposes. However, many men find it worthwhile, as it blocks the hormone DHT, which is responsible for male pattern baldness. When this hormone is blocked, they can regrow their hair.
Scalp Micropigmentation
Scalp micropigmentation is a treatment that involves tattooing very small, hair-like marks on the scalp to give the appearance of a full head of hair. This is best suited for individuals experiencing permanent hair loss who are willing to accept a short hairstyle.
Low-Level Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy is a hair restoration treatment that uses lasers to stimulate new growth. It’s a very minimally invasive surgery with low-level lasers that do not cause much discomfort. It’s best to get this treatment done a couple of times to see full results.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy
Another type of therapy used to regrow the hair is platelet-rich plasma therapy. This works by utilising platelets in the blood to stimulate new growth, as these platelets contain growth factors that encourage the follicles to produce new hairs. Like low-level laser therapy, you should get this treatment a few times to see proper results.
A Hair Transplant
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves taking hair follicles from the donor area of the scalp and implanting them into the recipient area, where they take root and grow new hairs, leading to a full head of hair once more. There are several types of hair transplant procedures, with the two most common being FUT (follicular unit transplantation) and FUE (follicular unit extraction). FUE is generally the recommended option, as it’s a process that involves extracting individual follicles for a more natural result.
Is a Hair Transplant Right for Gabapentin Hair Loss?
Gabapentin hair loss is typically temporary, with patients often experiencing hair regrowth once they stop taking the medication. As such, a permanent hair restoration solution like a hair transplant probably is not the best route forward.
Hair transplants are most successful when used for androgenetic alopecia, a genetic type of hair loss that affects both men and women. To determine if you are a suitable candidate for a hair transplant, it is best to consult directly with a hair surgery expert. If you want to see what a hair transplant can do, head to our patients gallery.
In Summary
There is a link between gabapentin and hair loss, but there is not yet enough research to understand why it causes hair loss in some people. It is a rare side effect that most people who take gabapentin do not have to worry about. However, if you do experience hair loss after taking gabapentin, speak to your doctor as soon as possible, as they can devise an action plan to reverse the hair loss, whether that’s adjusting the dosage or switching medications.
Sources:
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/21561-gabapentin
- https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/gabapentin/about-gabapentin/#:~:text=In%20epilepsy%2C%20it’s%20thought%20that,Gabapentin%20is%20available%20on%20prescription.
- https://www.jpsmjournal.com/article/S0885-39240800650-7/fulltext
- https://www.healthline.com/health/stages-of-hair-growth